CAISO: The state of grid-scale battery energy storage in 2024
Executive Summary
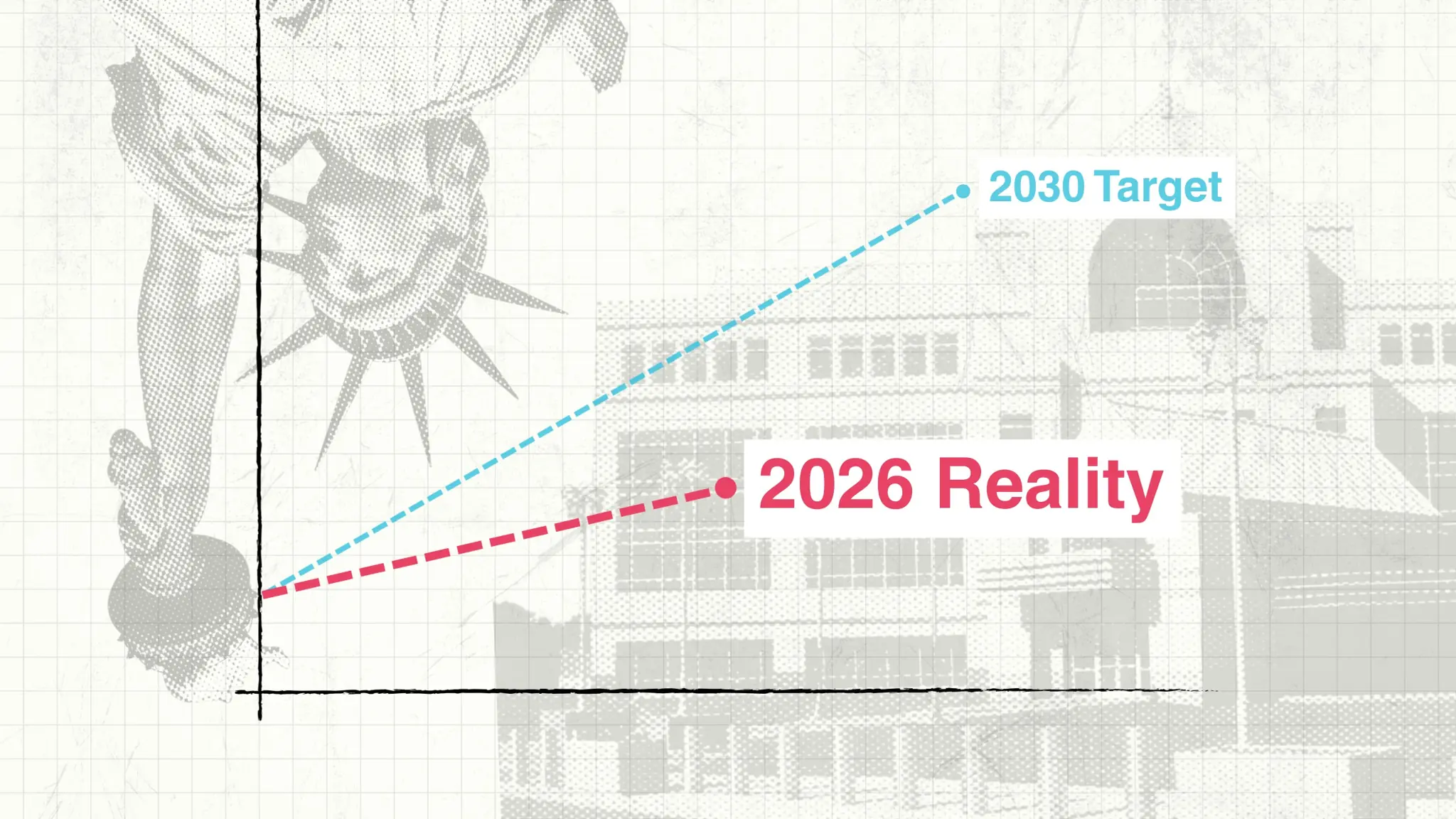
- CAISO will have 12 GW of operational battery energy storage by the end of 2024, up from just 470 MW in 2020.
- The five largest sites - including Edwards & Sanborn, and Moss Landing - will account for 25% of total BESS capacity in California.
- Another 5.6 GW is set to come online in 2025, driven by large-scale hybrid projects.
Subscribers to Modo Energy’s Research will also find out:
- How SP15 dominates CAISO’s battery buildout and why its solar resources drive price volatility.
- Which major battery projects are currently in testing and expected to reach commercial operation in 2025.
- How CAISO’s Resource Adequacy market is shaping battery investment and financing decisions.
To get full access to Modo Energy’s Research, book a call with a member of the team today.
Introduction
The total rated power of battery energy storage across the US could be as high as 140 GW by 2030. CAISO and ERCOT have led the way and are set to deliver the bulk of this forecast.
But how much of this capacity is commercially operational today? What are the biggest battery sites in CAISO in 2024? And which batteries are coming into the picture in 2025?
Download
Already a subscriber?
Log in